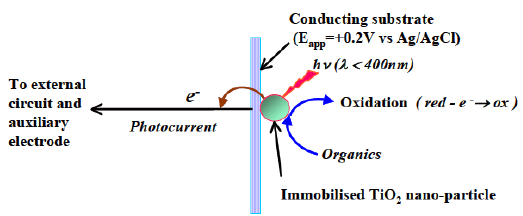
The primary driver of the peCOD method chemistry is advanced oxidation induced by photocatalysis with Titanium Dioxide (TiO2). Pure TiO2 is only photo-active at wavelengths below 380 nm. This is because a certain amount of light energy is required to bump the electrons around and cause the behaviors that we associate with photocatalysis. The UV LED in the PeCOD® COD Analyzer operates at a peak wavelength of 365 nm, with a minimum 360 nm and maximum 370 nm, ensuring that efficient photocatalysis is achieved.
Related Posts