Determining the Conductance of Water Samples
Method Abstract #77
Scope and Application
This method determines the conductance of water samples. This method conforms to Standard Method 2510 B, US EPA 120.1, ASTM D1125, ISO 7888 and EN 27888.
Method Summary
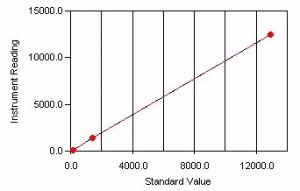
A conductivity cell consisting of two plates is submerged into a solution and a voltage is passed across the two plates. Ions in the solution are attracted to the plate of opposite charge and move between the two plates depending on the resistance of the solution. Conductivity is then expressed as the reciprocal of the electrical resistance and is commonly reported in units of microsiemens (µS). Prior to sample analysis, a calibration is performed using standard potassium chloride solution. The conductivity reading is then read directly from the conductivity meter.
Sample Calibration Curve
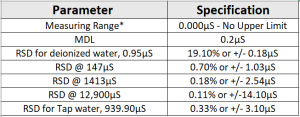
Method Performance
*Data for this measuring range was obtained using laboratory prepared standards formulated from potassium chloride. The measuring range may be increased by using auto-dilution.
RSD Values are better then those specified in Standard Methods.
The MANTECH C10 Conductivity meter and associate temperature compensated probe has a range of 0.000µS/cm to 2,000mS/cm.