Sulfate in Ethanol by Potentiometric Titration
Method Abstract #117
Scope and Application
This method conforms to ASTM D 7318. This method allows for the potentiometric determination of an endpoint in the direct titration of sulfate with 0.00035 N lead perchlorate, Pb(ClO4)2(aq).
Sulfate, SO42-, is an inorganic salt ion and is the main contaminant in fuel ethanol as the precipitating salts can cause injector deposits, as well as failure in the fuel line in automobiles. Oxygenated fuels can produce corrosion in-vehicle components in contact with the fuel and even at a low contaminate level, sulfate can enhance this corrosion process, decreasing the lifespan of the metal parts in the fuel system.
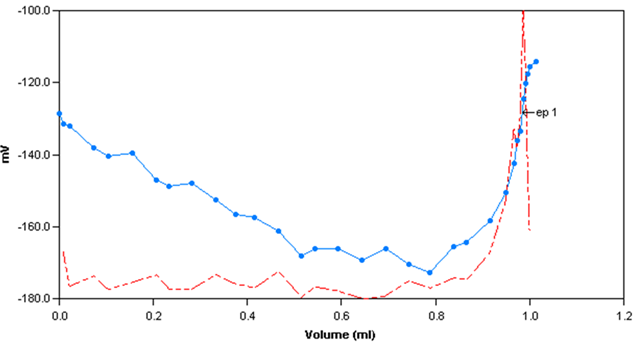
Sample Titration Curve
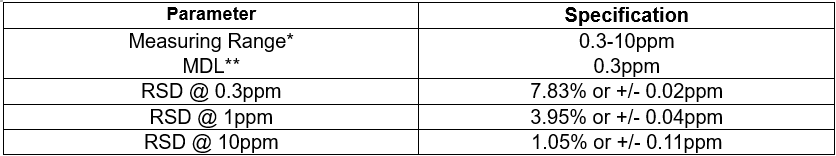
Method Performance
Related Posts
